Contents
- 1 Components Required
- 1.1 DHT22 Temperature and Humidity Sensor
- 1.2 ESP-01 ESP8266 WiFi Module
- 2 Circuit Diagram and Explanation
- 3 Program
- 3.1 DHT22 Library
- 4 Working
In this tutorial we are going to make a weather station that will tell us temperature, humidity and heat index of a particular location. It will show these values in a web browser. You can monitor these data by entering the IP address in a mobile, computer or any other device which supports a web browser.
This project is done using Arduino Uno, ESP8266 and DHT22 sensor. DHT22 sensor will read temperature and humidity information. ESP8266 WiFi module is used to establish network communication. Arduino is the core of this project which will read data from DHT22 sensor and sending it to a browser whenever a request is received. Arduino + ESP8266 is programmed to act as a web server.
Components Required
- DHT22 Temperature and Humidity Sensor
- ESP8266 WiFi Module
- Arduino Uno
- 1KΩ resistors
- Breadboard
DHT22 Temperature and Humidity Sensor
 |
| HT22 Temperature and Humidity Sensor |
It uses digital signal collecting technique and humidity sensing technology. It’s sensing elements are connected with an 8-bit microcontroller. DHT sensors are small in size, consumes low power and has the long transmission distance using one wire bus (20m).
DHT22 sensor consists of two sections, one for humidity sensing (capacitive humidity sensor) and another for temperature sensing (thermistor). The microcontroller inside the sensor reads both relative humidity and temperature from respective sensors. Then sends it via the output pin after converting to digital format.
ESP-01 ESP8266 WiFi Module
 |
| ESP-01 ESP8266 Module |
ESP-01 is the one of the most popular ESP8266 module available in the market. ESP8266 is a self contained SoC with integrated TCP/IP stack which helps any microcontroller having UART to access a wifi network. It can act as both WiFi access point as well as a WiFi client. It is pre-programmed with AT commands, so we can easily access and configure it using a microcontroller.
ESP8266 runs on 3.3V and its input pins are not 5V tolerant. So we need to reduce the 5V output of the Arduino Tx pin to 3.3V by using voltage dividing resistors to connect to Rx pin of ESP8266 module. Arduino TTL input pins will detect 3.3V as logic high, so we can directly connect 3.3V output of ESP8266 Tx to Arduino Rx pin.
Circuit Diagram and Explanation
First of all we will connect DHT22 sensor with the Arduino Uno. Connect the 5V and the ground of the DHT22 to the 5V and ground output of Arduino. Then connect the data pin of the DHT22 to the pin 8 of the Arduino.
Then we will connect the ESP8266 with Arduino. Note that ESP8266 is a 3.3V device, so make sure that you are connecting 3.3V supply to it. Connect the VCC and CH_PD pin of ESP8266 with 3.3V output of Arduino and also make the ground common. Its input pins are not 5V tolerant. So we need to reduce the 5V output of the Arduino Tx pin to 3.3V by using voltage dividing resistors to connect to Rx pin of ESP8266 module. Arduino TTL input pins will detect 3.3V as logic high, so we can directly connect 3.3V output of ESP8266 Tx to Arduino Rx pin.
Note : I used a potentiometer to generate 3.3V from 5V instead of three 1KΩ resistors.
Program
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> //including the software serial UART library which will make the digital pins as TX and RX
#include "DHT.h" //including the DHT22 library
#define DHTPIN 8 //Declaring pin 8 of arduino to communicate with DHT22
#define DHTTYPE DHT22 //Defining type of DHT sensor we are using (DHT22 or DHT11)
#define DEBUG true
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE); //Declaring a variable named dht
SoftwareSerial esp8266(2,3); //Connect the TX pin of ESP8266 to pin 2 of Arduino and RX pin of ESP8266 to pin 3 of Arduino.
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
esp8266.begin(9600); // Set the baud rate of serial communication
dht.begin(); //This will initiate receiving data from DHT22
sendData("AT+RST\r\n",2000,DEBUG); // Reset the module
sendData("AT+CWMODE=2\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // Configure ESP8266 as an access point
sendData("AT+CIFSR\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // Get the IP address of ESP8266
sendData("AT+CIPMUX=1\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // Configure ESP8266 for multiple connections
sendData("AT+CIPSERVER=1,80\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // Start TCP server at port 80
}
void loop()
{
float hum = dht.readHumidity(); //Reading humidity and storing in hum
float temp = dht.readTemperature(); //Reading temperature in celsius and storing in temp
// Check if any reads failed and exit early (to try again)
float f = dht.readTemperature(true);
if (isnan(hum) || isnan(temp)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
float hi = dht.computeHeatIndex(f, hum); // Computing heat index in Fahrenheit
float hiDegC = dht.convertFtoC(hi); // Converting heat index to degree centigrade
if(esp8266.available()) // If any data is available to read (only when we request data through browser)
{
if(esp8266.find("+IPD,")) // Validating the request by finding "+IPD" in the received data
{
delay(1000);
int connectionId = esp8266.read()-48; // Subtracting 48 from the character to get the connection id.
String webpage = "<h1>Arduino Weather Station</h1>"; // Creating a string named webpage and storing the data in it.
webpage += "<h3>Temperature: ";
webpage += temp; //This will show the temperature on the webpage.
webpage += "*C";
webpage += "</h3>";
webpage += "<h3>Temperature: ";
webpage += f;
webpage += "F";
webpage += "</h3>";
webpage += "<h3>Humidity: ";
webpage += hum;
webpage += "%";
webpage += "</h3>";
webpage += "<h3>Heat index: ";
webpage += hiDegC;
webpage += "*C";
webpage += "</h3>";
webpage += "<h3>Heat index: ";
webpage += hi;
webpage += "F";
webpage += "</h3>";
String cipSend = "AT+CIPSEND=";
cipSend += connectionId;
cipSend += ",";
cipSend +=webpage.length();
cipSend +="\r\n";
sendData(cipSend,1000,DEBUG);
sendData(webpage,1000,DEBUG); // Sending temperature and humidity information to browser
//The following three commands will close the connection
String closeCommand = "AT+CIPCLOSE=";
closeCommand+=connectionId; // append connection id
closeCommand+="\r\n";
sendData(closeCommand,3000,DEBUG); // Sending the close command to the sendData function to execute
}
}
}
//This function will send the data to the webpage
String sendData(String command, const int timeout, boolean debug)
{
String response = "";
esp8266.print(command); // Sending command to ESP8266 module
long int time = millis(); // Waiting for sometime
while( (time+timeout) > millis())
{
while(esp8266.available()) // Checking whether the ESP8266 has received the data or not
{
char c = esp8266.read(); // Reading response from ESP8266
response+=c;
}
}
if(debug)
{
Serial.print(response);
}
return response;
}
DHT22 Library
You need to manually add DHT library to Arduino IDE as it is not included by default. You can ignore it if you already added it. Otherwise you can do following steps for that.
- Download DHT Library from here : DHT Sensor Library.
- Open Arduino IDE.
- Go to Sketch >> Include Library >> Add .ZIP Library
- Select the downloaded ZIP file and press Open.
Working
After uploading the code to Arduino, open the serial monitor from the Arduino IDE. It should show you the IP address as shown below.
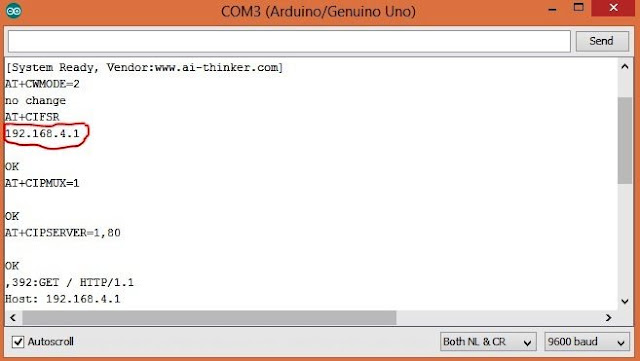 |
| ESP8266 – Arduino Web Server – IP Address |
Then connect your system to the access point created by ESP8266 module (ESP_xxxxxx). Enter the IP Address in your web browser (Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox). Now you can monitor temperature and humidity details.
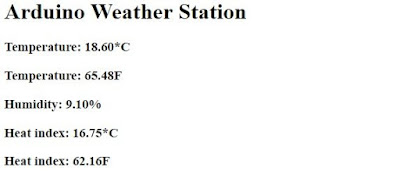 |
| Arduino Weather Station – Web Server – Output |
Note : You may change the default SSID (ESP_xxxxxx) of ESP8266 WiFi module by using AT+CWSAP command.




192.168.4.1 this ip address is not opening what i have to do???
ReplyDelete